Numerical Solution Technique: Difference between revisions
From WikiROMS
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Vertical and Horizontal Discretization== | ==Vertical and Horizontal Discretization== | ||
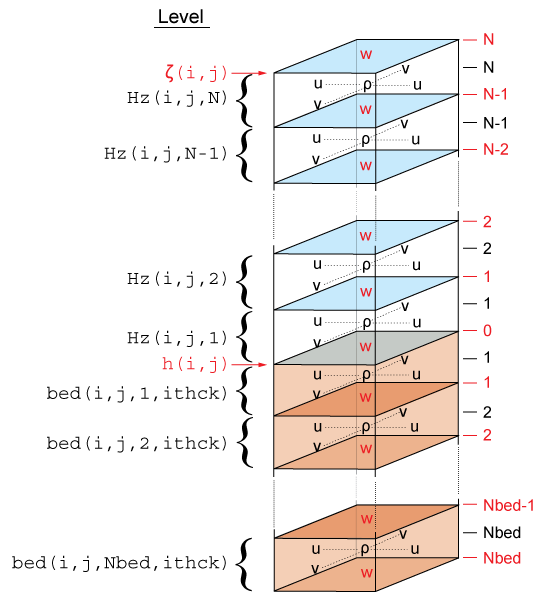
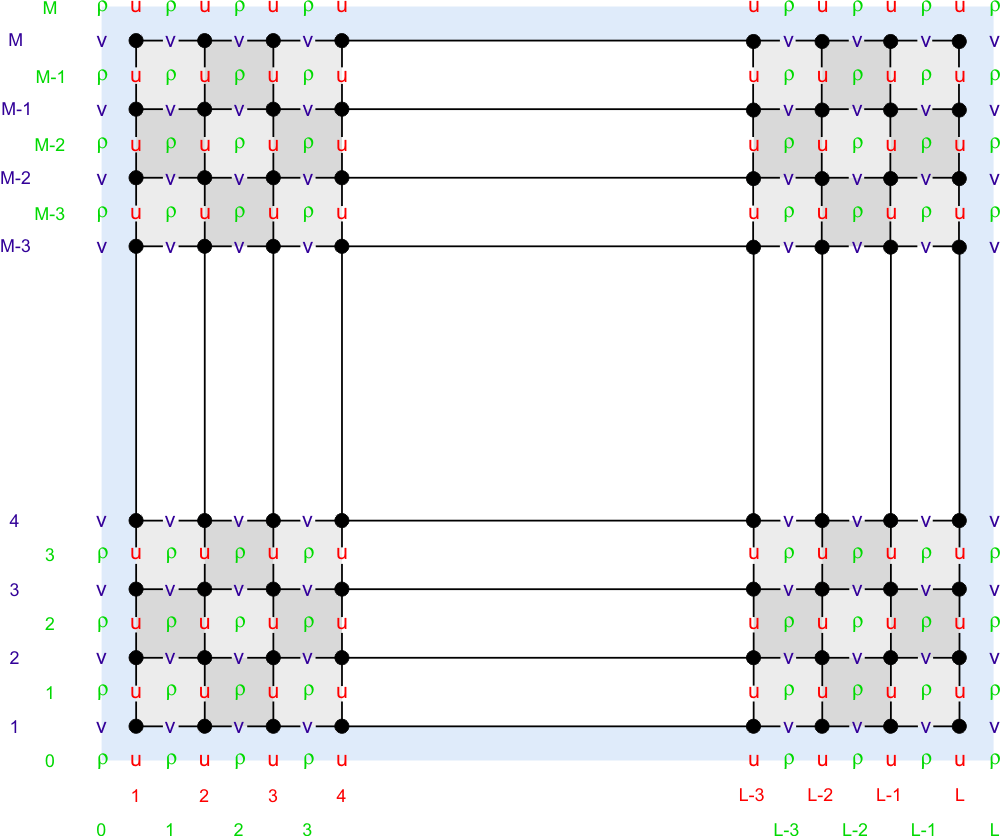
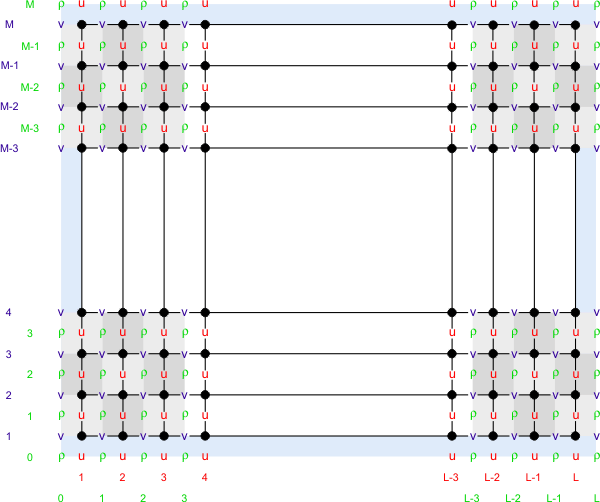
The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness (Hz) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum (u,v), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity (ω, w) and vertical mixing variables (Akt, Akv, etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell | The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness (Hz) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum (u,v), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity (ω, w) and vertical mixing variables (Akt, Akv, etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell. See diagram below. | ||
[[Image:vertical_grid.png|ROMS vertical grid]] | [[Image:vertical_grid.png|ROMS vertical grid]] | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 27 February 2008
Numerical Solution Technique
Vertical and Horizontal Discretization
The ROMS governing equations are discretized over variable topography using a stretched, terrain-following, vertical coordinate. As a result, each grid cell may have different level thickness (Hz) and volume. The model state variables are vertically staggered so that horizontal momentum (u,v), density, and tracers (active and passive) are located at the center of the grid cell. The vertical velocity (ω, w) and vertical mixing variables (Akt, Akv, etc) are located at the bottom and top faces of cell. See diagram below.