Difference between revisions of "TEST HEAD CASE"
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
|Critical Shear Stress | |Critical Shear Stress | ||
|<math>\tau_{c}</math> | |<math>\tau_{c}</math> | ||
|<math>0.05 \,N/m^{s}</ | |<math>0.05 \,N/m^{s}</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Bed Thickness | |Bed Thickness | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 11 April 2008
This test case checks the ability of a model to represent 1) simplified alongshore transport, 2) implementation of open boundary conditions, and 3) resuspension, transport, and deposition of suspended-sediment. This case is based on Signell and Geyer (1991) Journal of Geophysical Research 96(C2): 2561-2575.
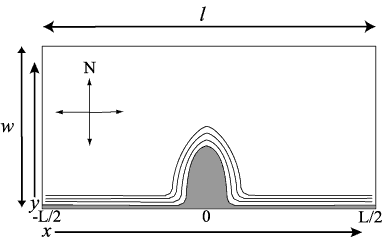
Domain
The model domain is open at the east and west ends, has a straight wall at the north end, and a parabolic headland along the south wall.
| Model Parameter | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Length (east-west) | 100000 m | |
| Width (north-south) | 50000 m | |
| Depth | 20 m |
Bottom Sediment
Single grain size on bottom:
| Size | 0.1 mm | |
| Density | ||
| Settling Velocity | 0.5 mm/s | |
| Critical Shear Stress | ||
| Bed Thickness | 0.005 m | |
| Erosion Rate |
Forcing
Coriolis f = 1.0 e-4
No heating/cooling
No wind
Initial Conditions
Salinity = 0
Temperature =
Bathymetry:
Depths increase linearly (slope = 0.0067) from a minimum depth of 2 m at all alongshore points from the southern land boundary offshore to a maximum depth of 20 m at a point 3 km offshore. Offshore of 3 km there is a constant depth of 20 m.
Boundary Conditions
North, south = walls with no fluxes, no friction
South wall = parabolic headland shape
Bottom roughness
Flow and elevation at western boundary is imposed.
Flow on eastern boundary is open radiation condition, or water level based, or Kelvin wave solution.
Flow and elevation, eastern/western boundaries:
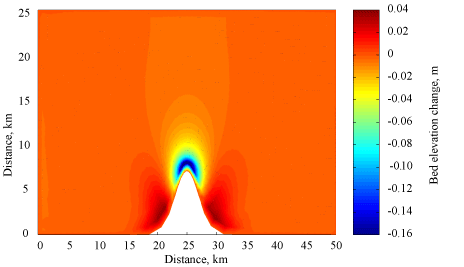
Results
Simulations were conducted for 3.0 days. Final bed thickness is shown in Figure 1.