ROMS-JEDI Implementation: Difference between revisions
From WikiROMS
Jump to navigationJump to search
Created page with "<div class="title">ROMS-JEDI Implementation</div> Most modern geophysical models can be connected to the '''JEDI''' framework, provided that the following predefined abstract..." (change visibility) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 19:09, 30 August 2023
ROMS-JEDI Implementation
Most modern geophysical models can be connected to the JEDI framework, provided that the following predefined abstract C++/Fortran classes or building blocks are coded:
| CLASS | Description |
|---|---|
| ErrorCovarinace | Background error covariance, training, and modeling (SABER: BUMP/NICAS) |
| Field/Fields | Elemental operators to manipulate a field or a set of fields to the model state/increment vector and metadata |
| Geometry | Application grid definition, including coordinates, metrics, parallel decomposition, and operators |
| GeometryIterator | Methods to set/get state fields over specified grid points in LETKF applications |
| Increment | Procedures to operate on the increment vector that extends/inherits from the Fields class |
| LinearModel | Initializes, run, and finalizes Tangent Linear and Adjoint model dynamical/numerical kernels |
| LinearVariableChange | Tangent/adjoint increment vector variables transformation from one field to another |
| Localization | Model Ensemble Localization (SABER: BUMP/NICAS) |
| Model | Initializes, run, and finalizes the Nonlinear model dynamical/numerical kernel |
| State | Procedures to operate on the state vector that extends/inherits from the Fields class |
| Trajectory | Methods to process the Nonlinear trajectory that linearizes the tangent linear and adjoint models |
| VariableChange | Nonlinear state vector variables transformation from one field to another |
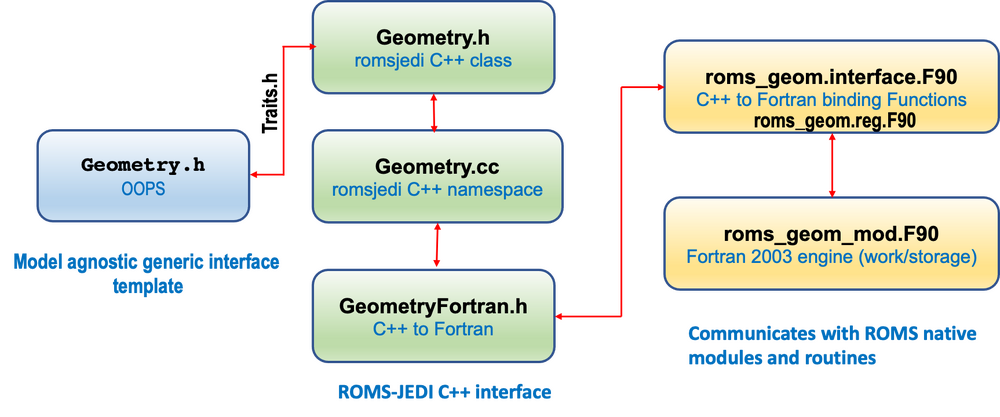
Code Design
Below is a diagram showing the interoperability mechanism for the Geometry Class that allows Fortran to invoke C++ function and vice versa for C++ to invoke Fortran procedures.